DOPPLER
Digital optimisation platform for district heating systems
This research project has been completed. Download the DOPPLER Publishable Final Report here.
Biomass and local heating networks are an important component of the energy transition. They use regional resources, strengthen local value creation, and can provide heat in a climate-friendly way. For such networks to run efficiently and with low emissions, generation, storage, distribution, and consumption must work together well, not just “by feel,” but based on data and with foresight. This is exactly where DOPPLER comes in.
Why optimisation is important
Many district heating systems are primarily regulated according to current demand. This is robust, but often leads to unfavorable operating points, such as unnecessarily high flow temperatures, increased distribution losses, greater stress on components, and overall lower efficiency. In addition, peak loads arise that can lead to oversizing (and higher investment costs). DOPPLER shows how digitalization and demand response help to reduce these effects without compromising customer comfort.
What DOPPLER has achieved
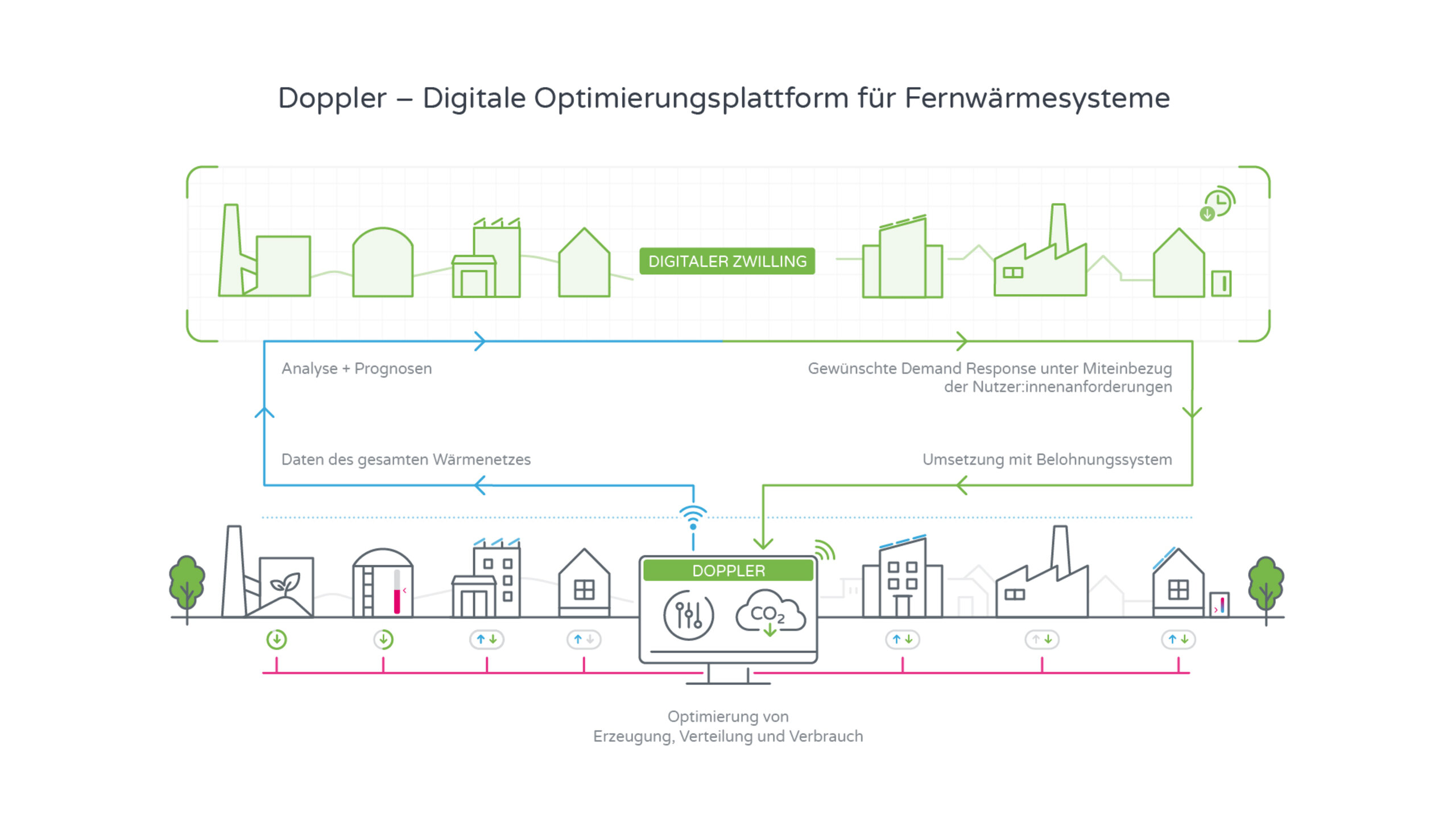
The project established an integrated platform that brings together the planning, operation, and optimisation of district heating networks, including the involvement of end customers. At its core is a digital twin (a “digital image” of the network) that combines real measurement data with simulation and optimisation. The project has thus demonstrated that model-based real-time optimisation works in practice when data connectivity, security logic, and user communication are implemented cleanly.
Key findings at a glance:
- Digital twins were implemented and calibrated for several networks in order to simulate network behavior realistically and test measures safely.
- A demand response control system for the flow temperature was developed and validated in Rohrbach: pilot operation/simulations showed an average reduction of approx. 5 Kelvin (5°C) while still meeting comfort requirements.
- Dashboards were set up as a shared “work and information space” for operators and end customers, ranging from technical KPIs to easy-to-understand efficiency indicators.
- The project provided practical insights into how to reliably integrate and harmonize heterogeneous data sources (OPC, APIs, CSV exports, manual readouts).
Approach: From data to optimisation
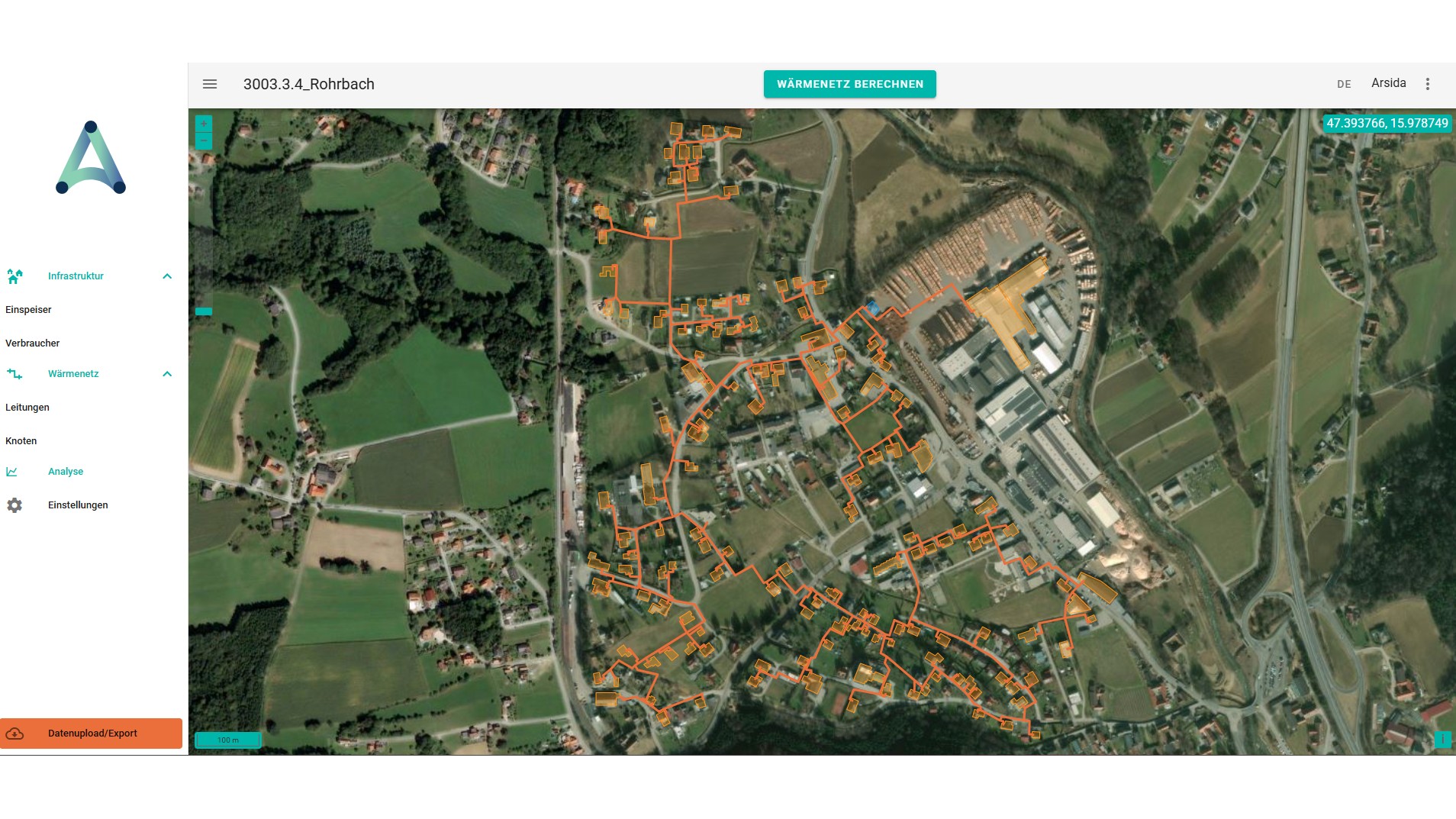
1) Digital twin as technical backbone
For the demonstration sites, the network structure (lines, transfer stations, nodes) was digitally recorded and linked to measurement data. These digital twins enable:
- Simulation of temperature and hydraulic behavior
- Comparison of “target/actual” for error and potential analysis
- Reliable evaluation of control and optimisation measures prior to deployment in real-world operation
2) Real-time data & interfaces – robust rather than perfect
In practice, networks vary greatly, with different control systems, different data formats, and different rules for data access. DOPPLER has therefore implemented several integration methods (including OPC, HTTPS APIs, CSV exports, periodic readouts). Important factors here were buffering, timestamp consistency, plausibility checks, and signal harmonisation (e.g., different names for the same measured variables).
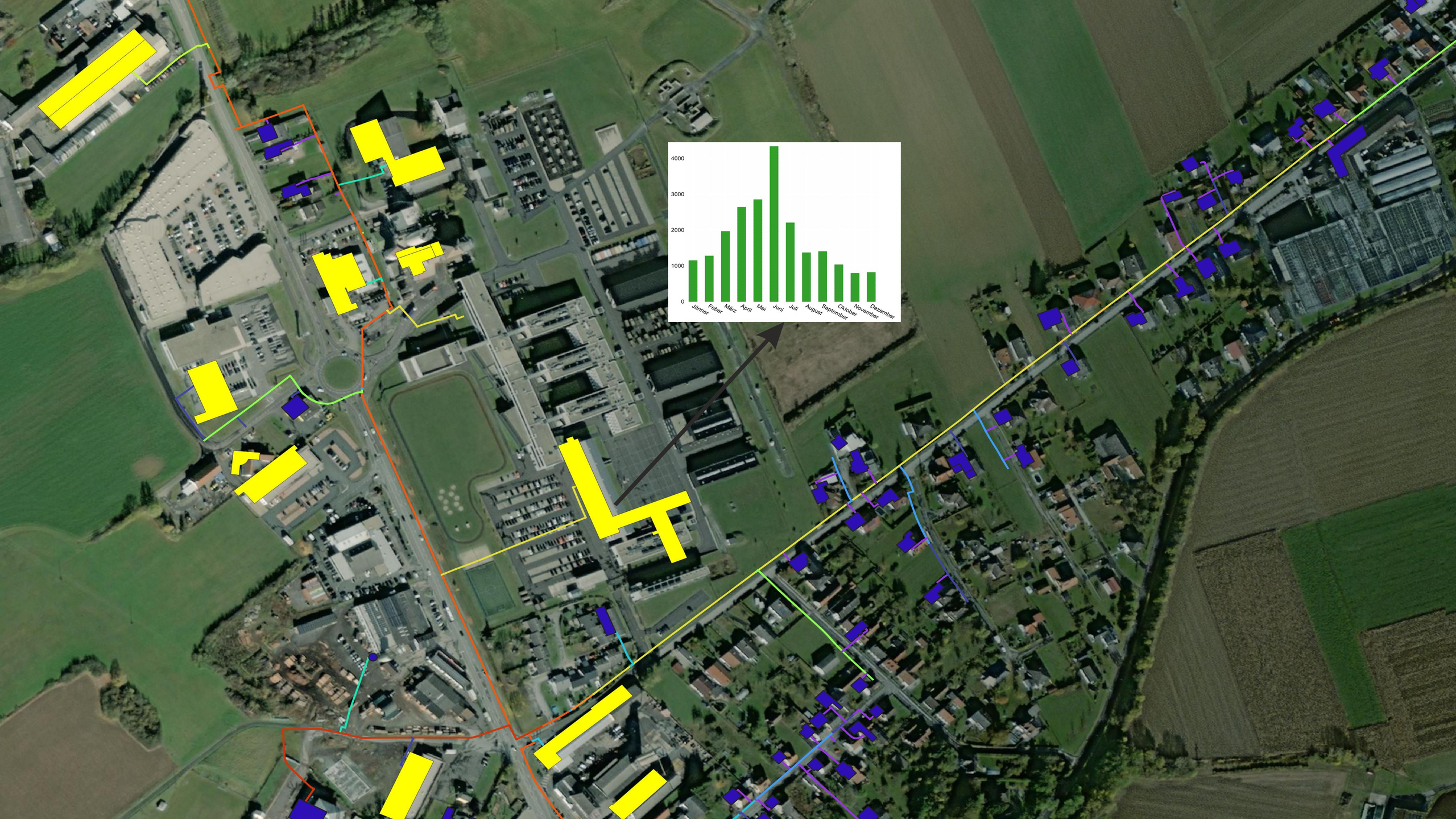
3) Optimisation of the flow temperature in Rohrbach
One highlight was the development of a control system that continuously calculates the lowest possible flow temperature that still reliably supplies all consumers. This reduces distribution losses and smooths operation. In pilot tests, a reduction of approximately 5 Kelvin (5°C) was achieved, stable, with safety limits, filtering against measurement noise, and fallback strategies in case of data gaps.
4) Optimisation on the generation side
In addition, a predictive, model-based control system (model predictive control) was investigated for the Rohrbach heating plant. Such approaches can make operation more “goal-oriented” (e.g., smoother, closer to the efficient operating point), but the benefits depend heavily on the plant structure and are typically greatest when there are multiple heat sources or greater flexibility.
Involvement of end customers: understandable, voluntary, effective
DOPPLER not only took end customers into account, but also actively involved them through visualisation, feedback, and motivation. A survey in Güssing showed a generally high willingness to be flexible if comfort is maintained:
- approximately 68% indicated a willingness to be more flexible with regard to space heating,
- approximately 58% for hot water (acceptance is lower here if it causes noticeable restrictions)
Gamification elements were tested in workshops: ranking/benchmarking was received positively for the most part, while “collective benefit” symbols (e.g., tree metaphors) are particularly effective when the story behind them is clearly explained (cause and effect).
Demonstration in Austria
The platform and methods were demonstrated at four locations: Güssing, Mischendorf, Japons, and Rohrbach. Depending on the technical situation, digital twins, data connections, dashboards, and optimisation modules were implemented and validated specifically for each location.
Links:
The following model solutions were being developed in the DOPPLER project:
Digital twin for optimizing district heating networks
Gamification as an incentive for customer involvement in demand response measures
Business models for demand response measures in district heating networks
Media reports on the project
Optimised dimensioning and operational planning of district heating systems – TGA 2024 (special edition, german only)
The DOPPLER project is developing a system-wide platform for district heating planning and operation that integrates all components such as generation, distribution and consumption. The project is being carried out as part of the Green Energy Lab research initiative. (page 8)
To the article