UCERS
Greater involvement of participants and freely available data platform for energy communities of the future
This research project has been completed. Access the UCERS Results Fact Sheet or download the Publishable Final Report here.
The UCERS project (User-Centered Solutions for Digital and Sustainable Energy Communities responded to the legislative introduction of energy communities (EC) in Austria and the accompanying need for practical, technical, and social support mechanisms to implement these frameworks effectively. The overarching aim of UCERS was to develop, test, and evaluate user-centered solutions that could enable the establishment and scaling of digital and sustainable ECs. Through a multi-disciplinary and trans-sectoral consortium, the project combined digital tool development, empirical fieldwork, participatory research, and policy-relevant analysis. The project focused on electricity, as this was the primary domain supported by Austria´s initial legal framework and existing public infrastructure. While heating represents an important aspect of the energy transition and holds future potential for energy communities, its integration — particularly with respect to measurement and data infrastructure — remains at an earlier stage of development.
UCERS included
- the development of digital infrastructures to support EC operations;
- the implementation of real test environments for different building types and ownership models;
- the design of participatory and co-creative engagement processes;
- the development of an evaluation scheme to assess the EC contribution to environmental, economic and social sustainability;
- comparative and longitudinal analysis to capture evolving expectations, experiences and practices within the EC landscape;
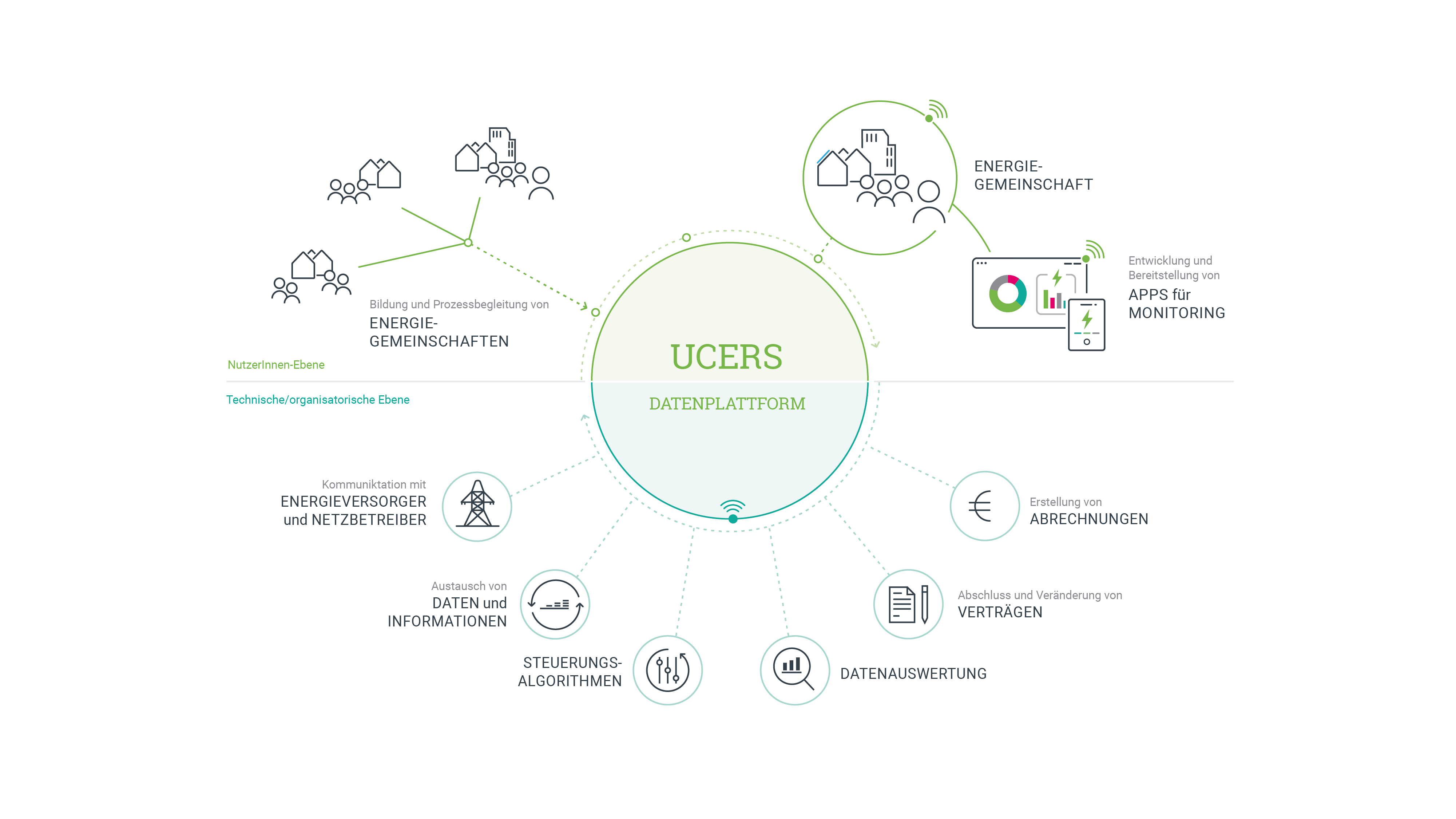
One of the key technological outcomes of the project was the Community Data Exchange Platform (CDEP), which provides a user-friendly interface for joining, managing and participating in ECs. The CDEP builds on the existing Austrian infrastructure and integrates information resources, project initiation tools and administrative functions such as contract management and member dashboards. In parallel, the Community Operation & Optimization Platform (COOP) was developed to support the ongoing technical coordination within the ECs. This system integrates monitoring, automation and optimization functions and was adapted to existing software solutions from technology partners. Both platforms were tested and refined through scenario-based trials and testbed implementations.
The empirical work within UCERS also included two major survey campaigns: A study focusing on the initial user expectations and motivations of EC participants – many of whom belonged to initiatives supported by project partners – showed that financial considerations were the main motivation for participating in ECs. Over time, however, respondents increasingly valued community, environmental and regional benefits. A later, more comprehensive study broadened this perspective by assessing sustainability performance in a more mature and diverse group of ECs. This included the development and application of a scoring scheme. The results of the survey reveal several important patterns: ECs performed consistently well in the areas of affordability and member satisfaction, often offering below-market electricity prices and promoting a positive perception of participation. However, there were notable gaps in implementation in the areas of inclusion, education and green initiatives. The assessment also identified discrepancies between stated priorities and operational practice — for example, environmental sustainability and regional development were often rated as very important, but the corresponding activities were not always implemented in practice.
Technical evaluations from the project’s test environments also highlighted the variability of EC performance. Even basic configurations without complex optimization achieved self-sufficiency rates of up to 40%, indicating that significant benefits can be achieved with relatively low barriers to entry. More advanced configurations, which included forecasting tools and energy storage showed higher self-consumption and system efficiency, although they require greater technical capacity and investment. Simulated scenarios also underpinned the potential of smart energy management and optimization of energy storage to improve overall performance.
The following model solutions were being developed in the UCERS project:
DATA PLATFORM FOR ENERGY COMMUNITIES
APP FOR ENERGY COMMUNITIES
CONTROLLER FOR ENERGY COMMUNITIES
Media reports on the project
Managing the community stream online – Der Standard
A software platform from the University of Applied Sciences Technikum Wien aims to make it easier for private individuals to enter the digital energy market.
To the article